Kollam's Chickenpox Outbreak: Symptoms and Vaccination
The recent outbreak of chickenpox in Kollam, Kerala, has put health authorities on high alert due to the rapid spread of the virus. With around 100 confirmed cases reported in just a few days, officials are emphasizing the importance of public awareness and preventive measures to control the situation.
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which spreads easily through sneezing, coughing, or close contact with an infected person. The post-monsoon humidity in Kollam provides ideal conditions for the virus to thrive. Health experts have noted that while the initial outbreak primarily affected children, adults are now at greater risk of infection.
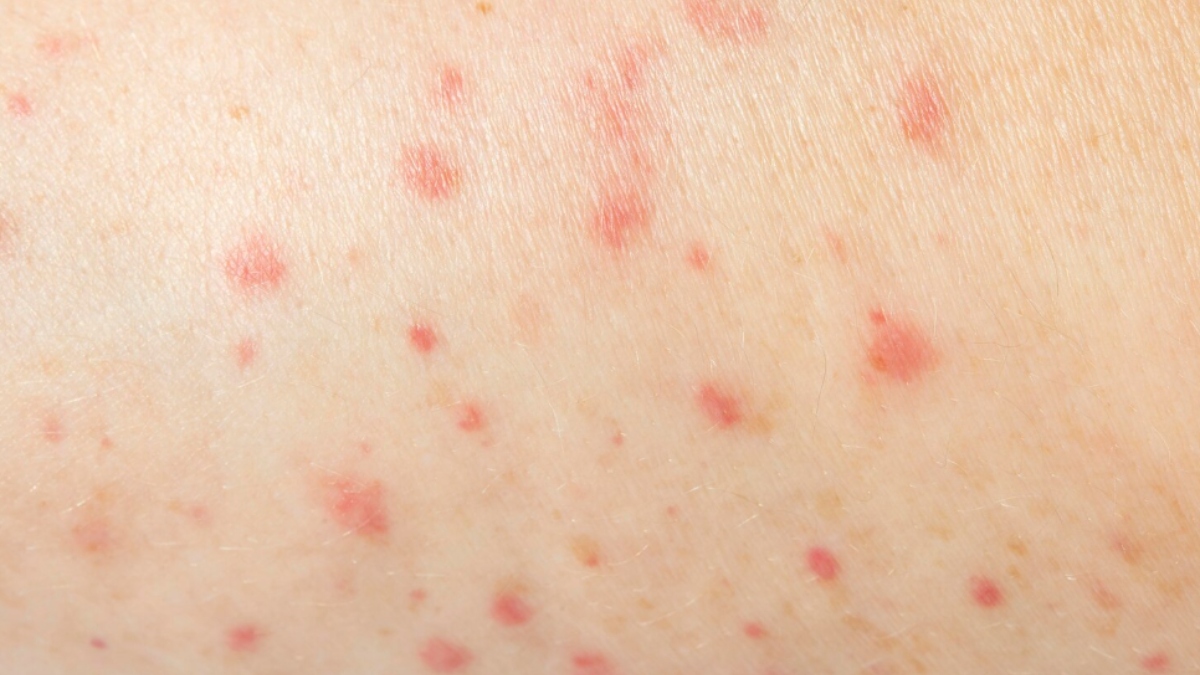
Dr. Manjusha Agarwal, a Senior Consultant in Internal Medicine, explains that chickenpox typically presents symptoms 10 to 21 days after exposure. Common signs include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, and an itchy rash that starts on the trunk and face before spreading. The rash progresses from red spots to fluid-filled blisters, which eventually crust over. New lesions can appear for days, and complications may arise, especially in infants, adults, pregnant individuals, and those with weakened immune systems.
Transmission of the varicella-zoster virus occurs through respiratory droplets and direct contact with the fluid from the blisters. It is contagious from approximately one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. Although prior infection provides lasting immunity, the virus can reactivate later in life as shingles.
Vaccination against chickenpox is crucial in preventing the disease and its complications. The varicella vaccine, a live attenuated vaccine, is recommended in two doses during childhood—first at 12 to 15 months and the second at 4 to 6 years. For unvaccinated adolescents and adults, two doses are advised, spaced 4 to 8 weeks apart. Studies show that two doses significantly reduce the risk of severe disease compared to just one dose.
While the vaccine is generally safe, contraindications include pregnancy and significant immunosuppression. Common side effects may include mild fever and local reactions, while severe reactions are rare. If you or your child have been exposed to chickenpox or are showing symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for vaccination, post-exposure options, and treatment.











