Nipah Virus Outbreak in India: Symptoms and Prevention
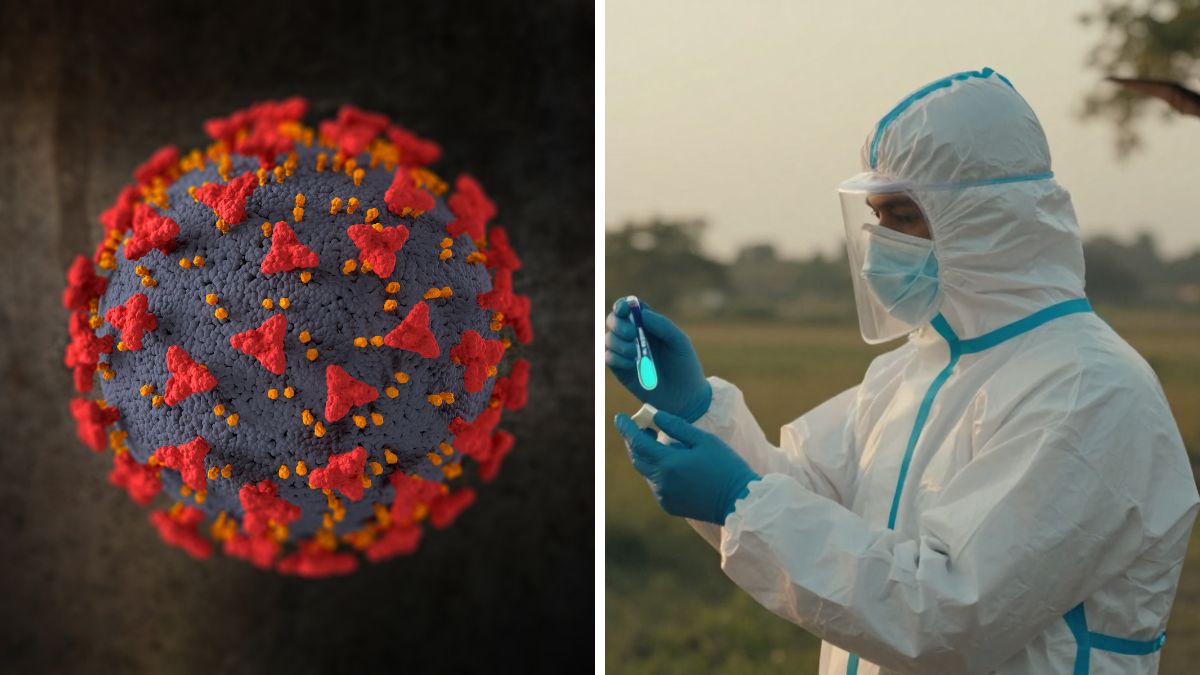
The recent outbreak of the Nipah virus in India, particularly with confirmed cases in West Bengal, has raised significant public concern. Nipah, a zoonotic virus primarily carried by fruit bats, poses serious health risks. While the virus is rare, its outbreaks require immediate public health responses due to the severity of the illness it can cause.
First identified during an outbreak in Malaysia in 1998, Nipah virus has since been reported in various regions of South and Southeast Asia. The transmission to humans can occur through direct contact with infected bats or consumption of contaminated food. In certain cases, human-to-human transmission has been documented, further complicating efforts to control the virus.
Symptoms of Nipah virus infection can manifest between 4 to 14 days after exposure, although in rare instances, the incubation period can extend up to 45 days. Early symptoms may mimic those of common viral infections, which often leads to challenges in identifying outbreaks promptly. Severe symptoms can escalate quickly, resulting in conditions like encephalitis and even coma.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates a fatality rate for Nipah virus infections ranging from 40% to 75%, depending on healthcare access and the effectiveness of the response measures. This high mortality rate underscores the importance of rapid identification and treatment of cases.
Preventative strategies are crucial in controlling the spread of the Nipah virus. Health authorities recommend being aware of the symptoms, avoiding contact with high-risk animals, and seeking medical attention as soon as symptoms appear. Public cooperation, accurate information dissemination, and adherence to science-based precautions remain vital in managing the outbreak.
As the situation evolves, the government is implementing comprehensive public health measures to contain the risk. Staying informed through credible sources and maintaining proper hygiene can empower individuals and communities to protect themselves against this serious health threat.
In conclusion, the Nipah virus outbreak is a reminder of the need for vigilance and preparedness in public health. By understanding the virus, its symptoms, and taking proactive measures, we can effectively mitigate its impact on our communities.